-
Medical care
- Premium programs
- Foreign clients
- For companies
- Price list
- Our doctors
- Gallery
- News
- Jobs
- Contacts






















Other services
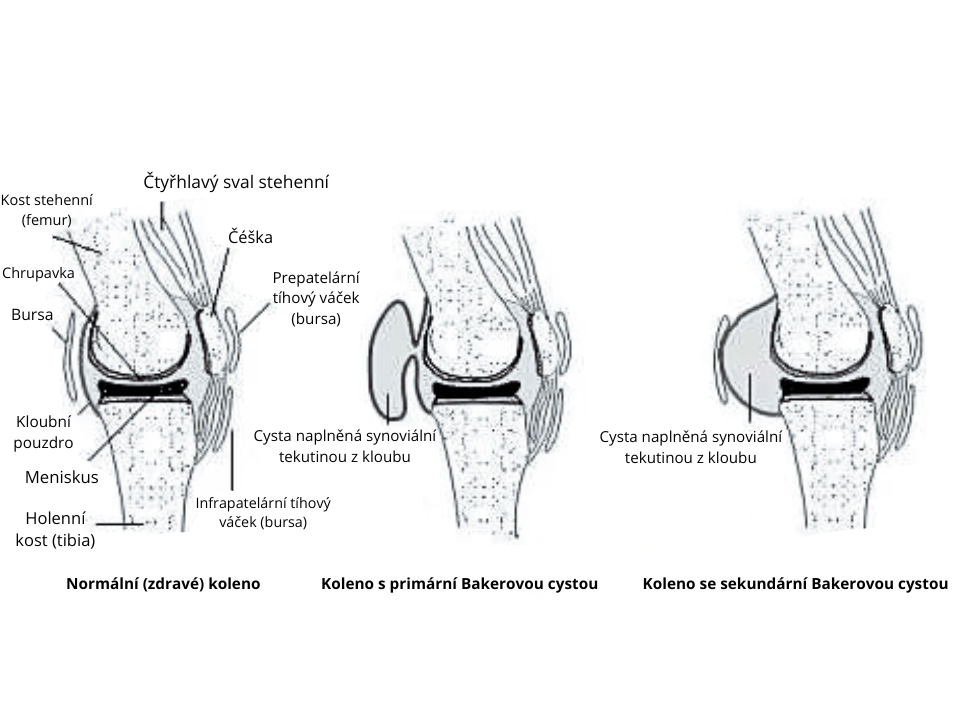
Baker's pseudocyst (cyst) is a soft formation located in the popliteal fossa. It is filled with synovial fluid, which is a common part of the knee joint. The cyst can be small and cause no symptoms, but it can also grow and cause pain, swelling and limitation of knee movement.
The cause of a Baker's pseudocyst is not completely known, but it is thought to be due to a malfunction of the connection between the knee joint and the popliteal bursa. These connections may be damaged by injury, inflammation or chronic overuse of the knee.
Symptoms of Baker's pseudocyst may be as follows:
Diagnosis of Baker's pseudocyst is based on clinical examination and imaging methods such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging or X-ray. Ultrasound is the most commonly used method for diagnosing Baker's pseudocyst.
Treatment of Baker's pseudocyst depends on its size and symptoms. Small cysts that do not cause any discomfort may not require any treatment. Larger cysts that cause pain or limitation of movement may be treated with medication or surgery.
Medications that are used to treat Baker's pseudocyst are usually non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen. These medications help reduce inflammation and pain. In some cases, it may be necessary to use corticosteroids, which have a stronger anti-inflammatory effect.
Surgical treatment of a Baker's pseudocyst is performed if medication does not work or if the cyst is causing severe discomfort.
Surgery usually involves suctioning fluid from the cyst. In some cases, it may be necessary to remove the cyst completely.
Suctioning fluid from a Baker's pseudocyst is an outpatient procedure that is done under local anesthesia.The doctor makes a small incision in the popliteal fossa and uses a needle to drain the fluid from the cyst.The procedure usually takes a few minutes and the patient can go home right after the procedure.
Postoperative care after suctioning fluid from a Baker's pseudocyst is usually simple.The patient should wear an elastic bandage on the knee for a few days to prevent swelling. He should also limit physical activity for several weeks.
In conclusion, Baker's pseudocyst is a common problem that can be caused by a variety of factors. If you have symptoms of Baker's pseudocyst, it is important to see a doctor for a diagnosis and to suggest appropriate treatment.
Photo: Baker's cyst. [www.cs.medlicker.com].






I was here for a comprehensive inspection and I can only recommend it, great attitude very nice treatment.






I've already used services of more specialists in Atoda Medical and every time I was satisfied with high quality service and very pleasant approach. All the same I can say about the nurses and receptionists who were always willing and quick to respond to any of my requests.